Why Does Swelling Occur in the Body?
Swelling occurs when blood circulation is diminished.
Blood carries that oxygen and nourishment we require to every corner of the body. The same blood then returns to the heart with carbon dioxide and waste produced by the cells. It is the action and movement of muscles that circulate the blood, but with insufficient muscle activity, blood circulation decreases, and swelling occurs. People who work at a desk all day often find that by day’s end their legs are swollen stiff due to a lack of muscular activity below the waist. Being at the farthest point from the heart, the calf muscles are a secondary pump, sending blood and other fluids back to the heart, and around the entire body. With total inactivity, gravity pulls fluids to the lower part of the body, resulting in swelling.
The Various Causes of Swelling
Too much salt. The human body requires a specific level of salt, and when too much salt is ingested, it modulates the level of salinity by storing water, which results in swelling. Alcohol is another cause of swelling, in this case due to the dilating effect of alcohol on the blood vessels, which causes a loss of water through the walls of the veins. In women, the hormones of the menstrual cycle can sometimes result in swelling, particularly before the period occurs, again due to the retention of fluid in the body. Lack of sleep, inactivity, stress and other factors are also common causes of swelling. Sudden and chronic swelling can each have different causes, as well.
Whether working sitting or standing, if the calves are not used, many people will experience swelling due to fluids collecting in the lower extremities. This effect can carry over into the evening hours, when a lack of elasticity in the calf muscles allows swelling to remain.
Acute swelling occurs after over-ingestion of salt or alcohol, due to hormonal activity during menstruation, lack of sleep or movement, and as a result of stress. This type of swelling can be alleviated by reducing the intake of salt and alcohol, resting, and stretching. Light cases of swelling are often cured by a good night’s sleep.
But there is also chronic swelling. When this occurs, it is possible there is a problem with the heart, liver or kidneys. Unlike acute swelling, chronic swelling can often be recognized with a finger pressure test, where the indentation of a finger pressed into the skin persists. Where this is observed, serious illness is a possibility, and a doctor should be consulted immediately.
Nutritional issues due to diet imbalances can also cause swelling, as can enlargement of veins in the calves and lower extremities. In some cases, such as lymphedema, surgical removal of lymph nodes is required.
Using Finger Pressure (Acupressure) to Reduce Swelling:
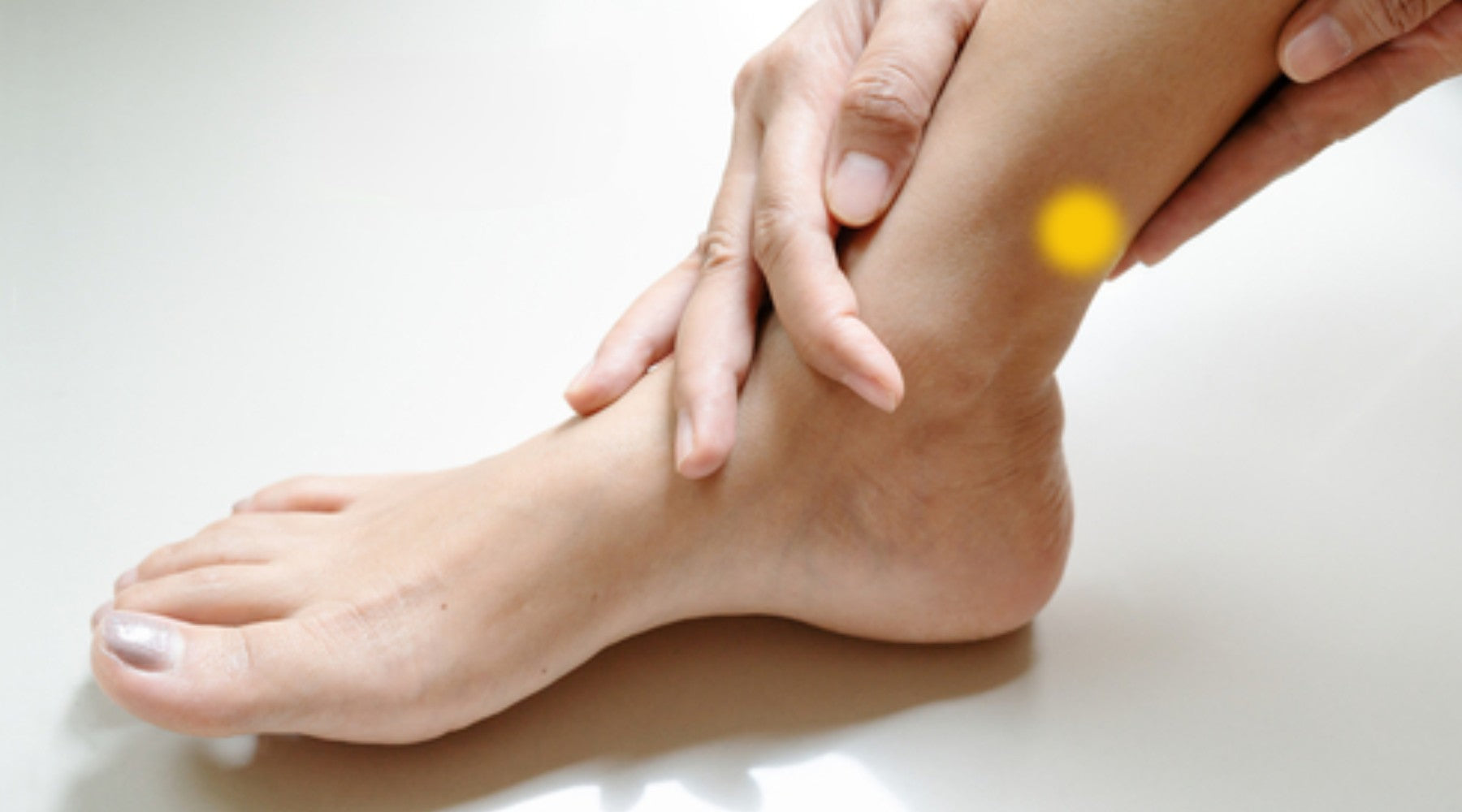
Upper Ankle Pressure Point
This pressure point is on the inside of the calf muscle just above the ankle bone.
Calf Pressure Points
These pressure points are located along the calf just to the outside of the shin bone.
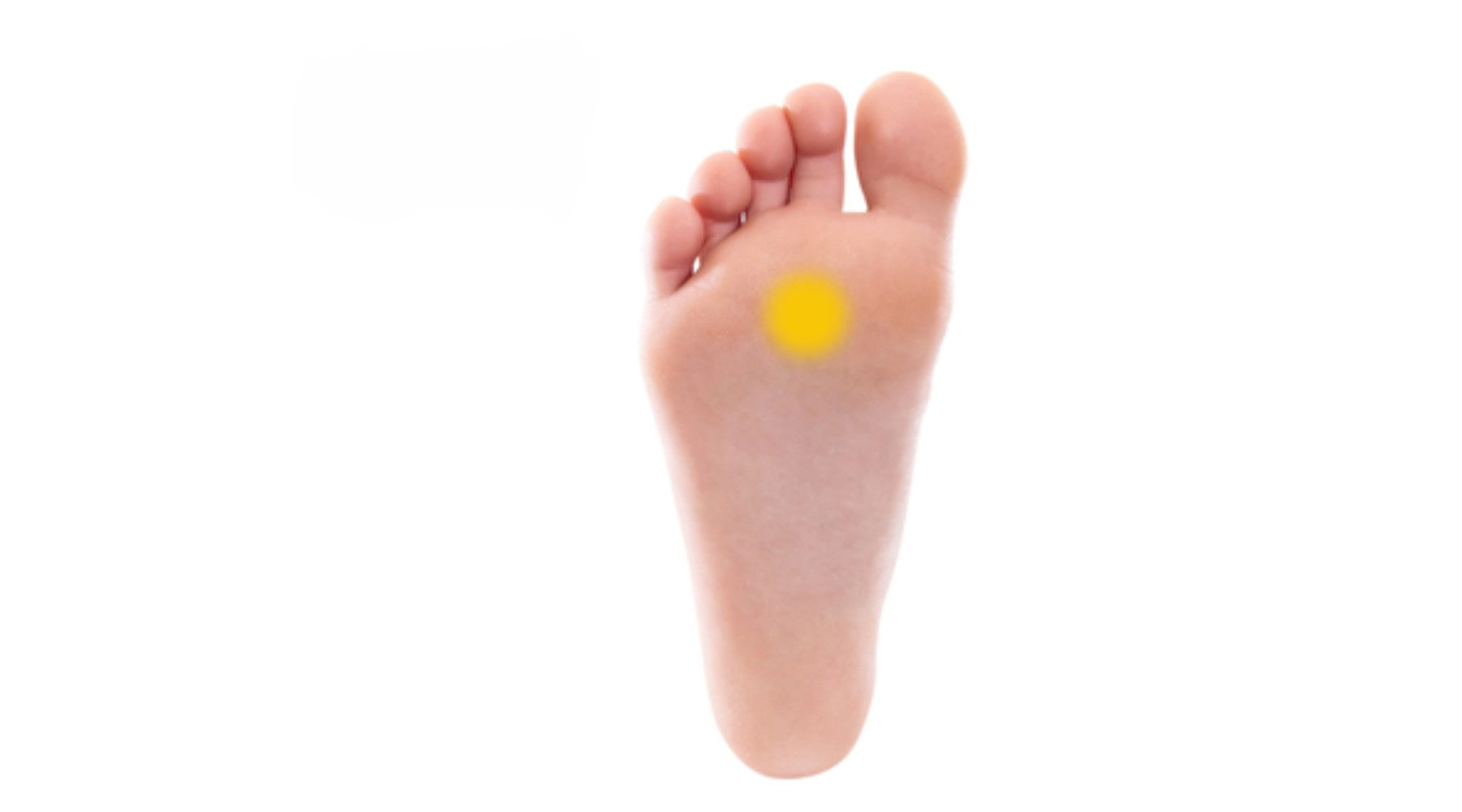
Pressure Point on the Base of the Foot
This pressure point is found in the middle of the instep, just behind the second and third toes.
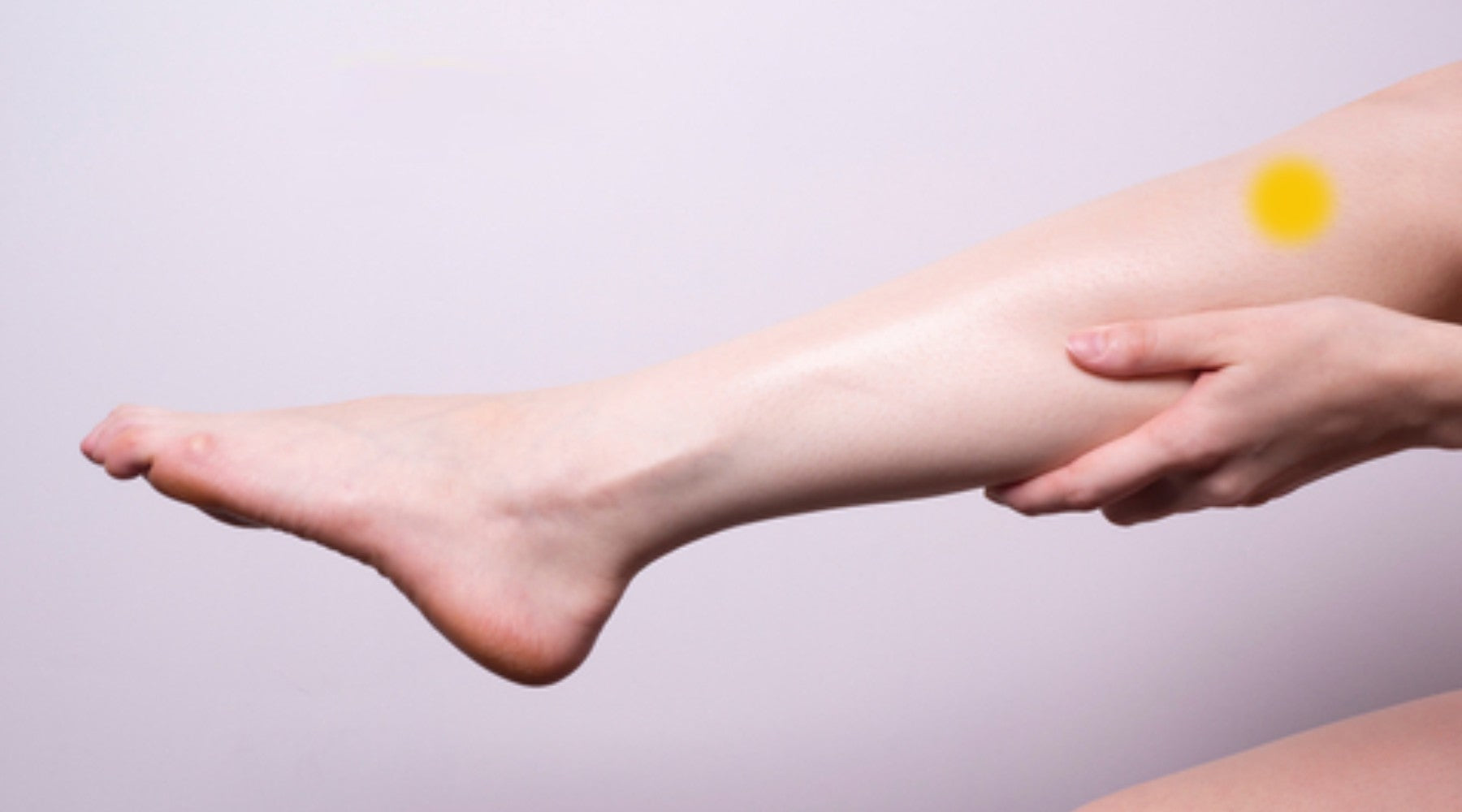
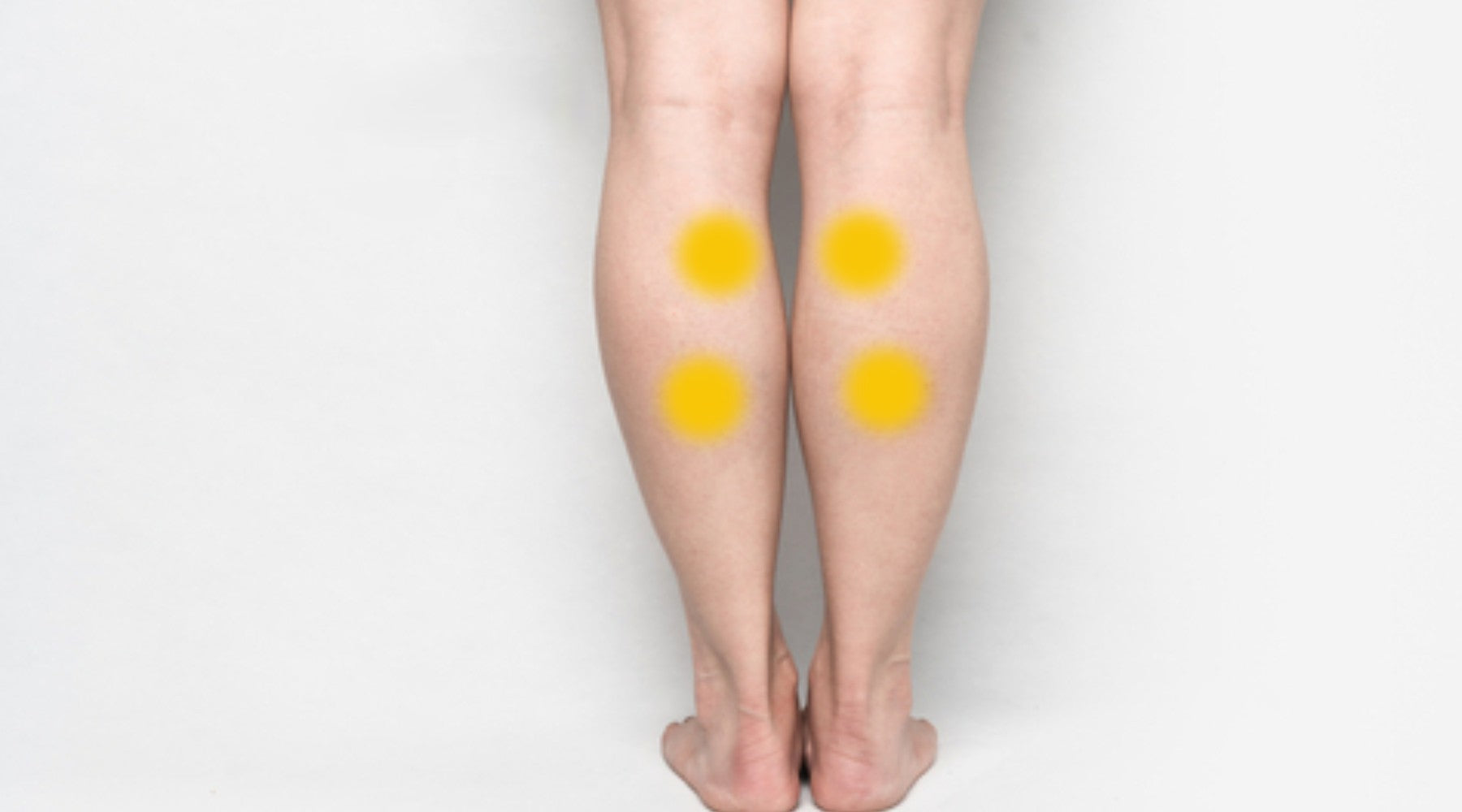
Pressure Points on the Back of the Calves
These pressure points run down the back of the calf muscle.
Pressure Point On the Top of the Foot
This pressure point is found on the top of the foot, on the webbing between the first and second toes.